Steps and Cornerstones
Sample injection (A) The first step is the metering an exact volume of analyte solution into a flowing stream of reagent. As the sample zone (red) moves downstream (B), dispersion process mixes the sample with reagent, forming a reaction product (yellow). The extent of mixing and the length of reaction time is controlled by the flow rate, by channel volume, and by channel geometry. Thus the time interval between the sample injection (A) and analyte detection (C) is reproducible. In this way, all samples are processed in exactly the same way, allowing comparison of standards with unknowns.
1.2.2.
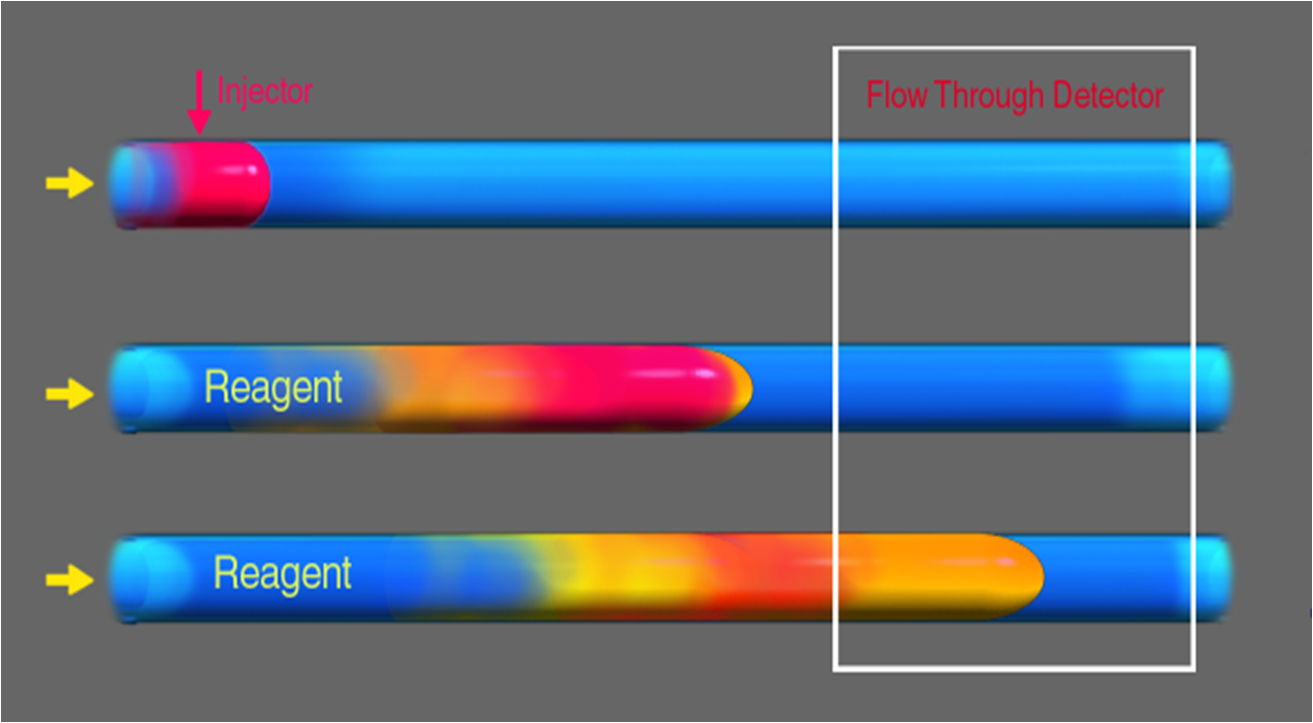
A
B
C
sample injection controlled dispersion reproducible timing